-

-
Restorer Ultimate for Mac
- Contents
- Index
- A -
Actions
Save recognized partition layout
Set raw file search options...
Apple CoreStorage/File Vault/Fusion Drive Volumes
- B -
Bad Sectors settings
Broken File Name options
Buttons
Change Raw File Search Options
- C -
Connect to Restorer settings
Allow connection from any address
Allow connection from the host
Contact Informaiton and Technical Support
Delete Recognized Partition Layout
Open Recognized Partition Layout
Save Recognized Partition Layout
Contextualt menu
Create a Virtual Volume Set or RAID
- D -
Data Recovery from Volume Sets and RAIDs
Data Recovery on HFS/HFS+ File System
Dialog boxes
There is not enough process memory...
- E -
Edit menu
- F -
File mask options
File menu
File Recovery on a Remote Computer
File Systems settings
Default encoding for Ext2/Ext3/Ext4/UFS volumes
Default encoding for HFS volumes
Find options
Finding Previous File Versions
- H -
Help menu
- I -
Image options
Introduction to Restorer Ultimate
- L -
Log settings
- M -
Main settings
Disable All Warnings and Confirmations
Show All Warnings and Confirmations
Memory Usage settings
Messages
Preview of the file is unavailable...
- N -
Nested and Non-Standard RAID Levels
- O -
Options
- P -
Panels
Panes
- Q -
- R -
RAID 6 Presets
RAID options
Recover Files from Deleted/Corrupted Logical Disks and Partitions
Recover Files from Existing Logical Disks
Recover Files from System Disk with SIP Enabled
Recover options
Do not recover hidden and system attributes
Recover all content of a selected folder, ignoring specified file mask:
Recover alternative data streams:
Recover real folders structure
Recover the entire path to the file object:
Region options
Restorer Ultimate Remote Emergency Engine
Restorer Ultimate Remote Engine
Restorer Ultimate Remote Engine Options
- S -
Scan options
Search options
Settings
Shortcut menu
Find Previous Versions of the File
Show Files Sorted by
- T -
Task List
Tools menu
- V -
View menu
Volume Sets, Stripe Sets, and Mirrors
- W -
Window
RAID5E
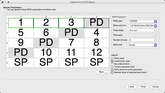
RAID 5E (where E stands for Enhanced) is a RAID 5 layout with an integrated hot-spare drive, where the spare drive is an active part of the block rotation scheme. An example of such RAID layout is in the table below:
|
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
1 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
PD |
|
2 |
5 |
6 |
PD |
4 |
|
3 |
9 |
PD |
7 |
8 |
|
4 |
PD |
10 |
11 |
12 |
|
5 |
SP |
SP |
SP |
SP |
where PD and SP stand for Parity of Data and Spare Part.
The RAID components are the images RAID5EDisk1.bin, RAID5EDisk2.bin, RAID5EDisk3.bin, and RAID5EDisk4.bin on the Device/Disk list.
To create a RAID 5E object
| 1 | Click Create Virtual RAID on the Task List |
| > | A Create Virtual RAID wizard will appear to guide you through the process of creating a RAID or Virtual volume set. |
| 2 | Select Virtual Block RAID Volume on the Create Virtual RAID dialog box then click the Next button |
Select Virtual Block RAID if you want to create a virtual RAID5E object.
| 3 | Select the required objects on the Available disks list and add them to the Selected disks list |
 RAID options
RAID options
|
Available disks |
List of disks available for creating virtual disk arrays |
|
Show Partitions |
If this check box is selected, Restorer Ultimate also shows partitions on hard drives |
|
Show as: |
Select the units in which you want to see object sizes. You may select, Bytes , Sectors , and Bytes and Sectors . |
|
Selected disks |
List of disks selected for creating virtual disk arrays |
|
Buttons |
|
|
Add |
Click this button to add the selected disk from the Available disks list to the Selected disks list |
|
Remove |
Click this button to remove the selected disk from the Selected disks list |
|
Remove All |
Click this button to remove all selected disks from the Selected disks list |
|
Move Up |
Click this button to move the selected disk one level up in the Selected disks list |
|
Move Down |
Click this button to move the selected disk one level down in the Selected disks list |
|
Add Missing Disk |
Click this button to add a virtual disk into virtual disk array that will be created |
Note: Components should be placed in the same order and the offsets should be specified as they were in the original volume set. If this order is incorrect, you must change it by using the Move Up and Move Down buttons.
If a component from the objects is absent (due to hardware failure, for example), you can add a "missing disk" to re-construct the RAID. The missing disk should be placed in the same order as in the original RAID structure.
Turning Disks On-Line and Off-Line on-the-fly
You may turn the objects in the virtual RAID or volume set on-line and off-line by selecting/clearing the On checkbox on the Create Virtual RAID dialog box . It may be useful, for example, if you need to see which disk is non-actual in a RAID5 or 6.
Actually, when you turn an object off-line, Restorer Ultimate substitutes it with a Missing Disk or Empty Space object.
Note: Restorer Ultimate does not write anything real on the disk. A missing disk is a virtual object that does not affect actual data on the drive.
| 4 | Select RAID 5E on the RAID type and other parameters for your RAID and click the Finish buttons |
The RAID block size parameter must be set the same as for the original volume set. If the order or Raid block size parameter is not correct, data on the parents will not be damaged, but the data cannot be recovered.
You may automatically find parameters for RAID 5 and 6. See the Finding RAID Parameters help page for details.
| > | A Virtual volume sets and RAIDs object will appear on the Device/Disk list panel |
The Virtual volume set or RAIDs object can now be processed like regular drives/volumes.
If Restorer Ultimate detects a valid file system on the newly created RAID object, a partition object will appear on the Device/Disk list panel.
Note: You may check how correctly you have reconstructed the original volume set or RAID. Find a file and preview it. If the file appears correct, you have created a correct RAID layout. The file should be large enough. For example, it should have size equal or larger to Block size*(Number of disks-Number of parity disks) for RAID 5 or 6.
The Description Files for RAID Configurations topic shows the RAID description file for this RAID configuration.
You also may check the RAID consistency, if necessary. See the Checking RAID Consistency help page for details.